
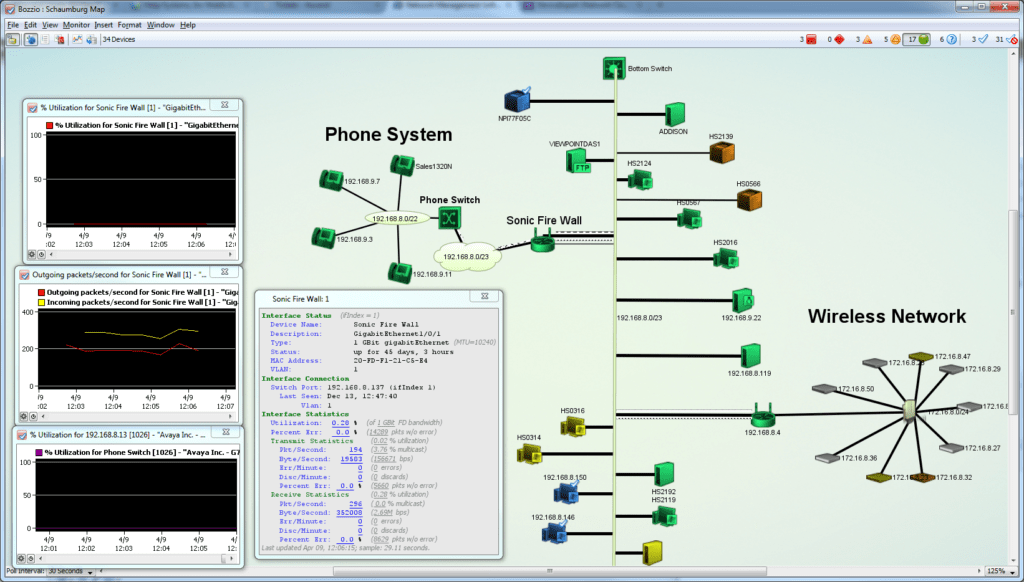
Select one or many icons and choose Format > Icon to pick a new icon. Change a device’s icon from a rectangle to a different icon or shape.Choose Format > Label (Ctl/Cmd-L) to see and edit the current template for that device’s label. Change the label that appears in the rectangle for a device to include more descriptive information.Remember that the network ovals represent subnets (address ranges), and act as the connecting points between devices. Lines between devices “rubberband” to preserve the interconnections. Drag items around to match the way you think of your network.Click the padlock icon in the upper-left corner to lock and unlock the map (when it’s locked, you’ll avoid inadvertent changes). You can make the map more informative by using the following tips: Intermapper’s Auto-Discovery and Auto-Layout do a basic job of showing what is connected to your network. Accept the defaults, and Intermapper will scan for devices that have addresses in that subnet range. Select one of the network ovals and choose Insert > Scan Network. Note that the devices appear on the map and turn green in a few moments, indicating that Intermapper is already testing them. Enter a few IP addresses or DNS names and click Add.In either case, you’ll see the Add Devices window.
#Intermapper automate manual
Create a new map and give it the name “Test Map 2.” Click the Manual Entry button, and then click Create, or add devices to an existing map by choosing Insert > Device.You can add devices manually by typing or pasting a list of DNS names or IP addresses. You must acknowledge them (see #10 below) to make them stop blinking. The device icon color represents its state: blinking red, orange, or yellow indicates problems.The network ovals represent the subnets that they attach to (a subnet is simply a range of IP addresses). This shows how the elements are connected. Change from the list to the Map View by choosing View > Map.Intermapper shows all the devices in a list with their IP address, DNS name (if available), probe type, and condition.Let auto-discovery complete or stop it after a few dozen devices have been found. To stop auto-discovery, click Cancel in the top of the map’s window.If you know the SNMP read-only community string for that device, enter it.
Intermapper defaults to using the local router, switch, or your own workstation. Enter the address of the starting point.
You’ll see the Automatic Device Discovery window appear.

Double click a map’s name to open the map in its own window.īuilding a Network Map with Auto-Discovery The Map List window shows all the maps that are available on your Intermapper server.
#Intermapper automate windows


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
